

That part of Alaska lying between meridians 160☀0' and 164☀0' west of Greenwich and in addition all of Unimak Island, but excluding Andronica Island That part of Alaska lying between meridians 156☀0' and 160☀0' west of Greenwich and in addition Andronica Island and all of Nagai Island.ĪLASKA ZONE 7 FIPSZONE:5007 UTM ZONES: 3 & 4 That part of Alaska lying between meridians 152☀0' and 156☀0' west of Greenwich and in addition Marmot Island, all of Afognak Island, all of the Barren Kenai Peninsula, but excluding Marmot Island, all of Afognak Island, all of the Barren Islands, all of Kalgin Island, all of Perry Island, and all of Esther Island. That part of Alaska lying between meridians 148☀0' and 152☀0' west of Greenwich and in addition all of Latouche Island, all of Evans Island, and all of the That part of Alaska lying between meridians 144☀0' and 148☀0' west of Greenwich and in addition all of Perry Island and all of Esther Island, but excludingĪll of Latouche Island, all of Evans Island, and all of the Kenai Peninsula.ĪLASKA ZONE 4 FIPSZONE:5004 UTM ZONES: 5 & 6 That part of Alaska lying between meridians 141☀0' and 144☀0' west of Greenwich. That part of Alaska lying east of meridian 141☀0' west of Greenwich. ADSZONE NUMBERS APPLY TO BOTH NAD27 AND NAD83 SYSTEMS, EXCEPT FOR MONTANA, NEBRASKA AND SOUTH CAROLINA WHICH LACK REFERENCE FOR THE NEW ZONES CREATED FOR NAD83ĪLASKA ZONE 1 FIPSZONE:5001 UTM ZONES: 8 & 9 NOTE: FIPSZONE NUMBERS ARE APPROPRIATE FOR BOTH NAD27 AND NAD83, UNLESS NOTED OTHERWISE. NE NV NH NJ NM NY NC ND OH OK OR PA RI SC SD TN TX UT VT VA WA WV WI WYĭownload this County/SPC/UTM Zone Data in MS Excel State Plane Zone Map FGDC Compliant Metadata Click on a state abbreviation below to jump to that state's data.ĪK AL AZ AR CA CO CT DE FL GA HI ID IL IN IA KS KY LA ME MD MA MI MN MS MO MT

(Use the ParamPlot or use what you know about when cosine equals zero). For what values will begin and end the trace of one petal.Plot the rose using ParamPlot and find the domain necessary to trace the entire curve without retracing any part of it.For six consecutive integer values of do the following four items. Note: Keep your work well organized and clearly labeled. So to find the area of the cardiod use the following command. Note that this gives you the right answer for a circle. This comes from the fact that the area in a thin wedge with radius and angle is The relationship between area and integrals in polar coordinates is a little strange the area inside a circle given (in polar coordinates) by is NOT just
#POLAR COORDS FULL#
You didn't get the full curve, change the domain until you do. To begin the animation, click on the plot and a new tool bar appears where the buttons resemble vcr controls. You can use ParamPlot to animate the plot. It is not always apparent what domain you need to get the full curve. Maple assumes that the first coordinate in the parametric plot is the radius and the second coordinates is the angle. In Maple you have to put square brackets around the curve and add the specification coords=polar. When you plot polar curves, you are usually assuming that is a function of the angle and is the parameter that describes the curve. When you use polar coordinates, you are defining the points in terms of polar coordinates. The basic idea is that you want to plot a set of points by giving their coordinates in pairs.

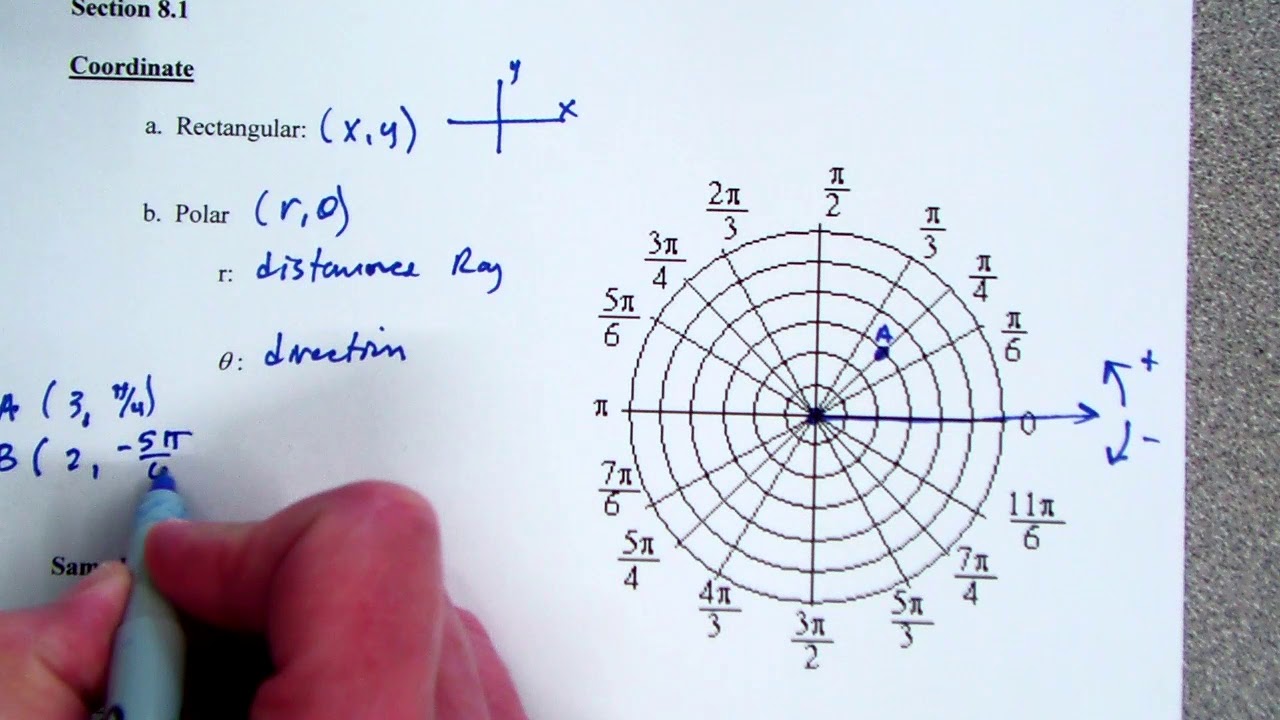
When you graph curves in polar coordinates, you are really working with parametric curves. However, using polar coordinates, curves with loops can appear as graphs of functions If a curve is a rectangular coordinate graph of a function, it cannot have any loops since, for a given value there can be at most one corresponding value. The use of polar coordinates allows for the analysis of families of curves difficult to handle through rectangular coordinates.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
